
Why is Eastern Europe still on the margins of colonial history? This historical silence is partly due to Western knowledge hegemony, but partly because Eastern Europeans have routinely positioned themselves as “always colonised” but “never having colonies”, thereby victimising themselves and denying their historical participation in global colonialism. Under “colonial rule” since Ottoman occupation (1526), but later as part of the Habsburg Empire, from the mid-19th century on, Hungarians increasingly sought in their contested, in-between semiperipheral position to open up to global colonialism.[1] This process may be demonstrated by the Asian expeditions of János Xántus (1825–1894), one of the most famed Hungarian natural scientists of the 19th century.
Zoologist and ethnographer, Xántus was founding contributor to the Hungarian National Museum, corresponding fellow of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (1859), founder and first director of the first Hungarian zoo (1866) and the Ethnographic Museum (1872), and founding member of the Hungarian Geographical Society (1872). He became a political refugee due to serving as officer in the failed 1848–49 Hungarian war of independence from the Habsburg Empire, in the 1850s and early 1860s he was drawn into North American expeditions, wrote about the culture and colonial subjugation of Indians, and developed a vast network to transfer specimens regularly back to Hungary. Upon his final return to Hungary, he was given the opportunity after the Austro-Hungarian compromise (1867) to participate in a series of imperial expeditions to East and Southeast Asia during 1868–71, which included Ceylon, Siam, Singapore, Java, China, Japan, Taiwan, The Philippines, and Borneo. Austrians had planned to open up to the East since 1860, but expeditions were delayed due to internal conflicts, the Prussian-Austrian war in 1866, and the execution of Archduke Ferdinand Maximilian in Mexico in 1967. The Austro-Hungarian expedition was to develop foreign trade relations and secure colonial positions in Southeast and East Asia with the opening of the Suez Canal (1869). However, the expedition did not fulfil its promise, and was torn by internal political tensions between Austrian and Hungarian counterparts: as a “1848er” independence fighter, Xántus struggled to have the expedition serve Hungarian national interests against Austrian suppression.
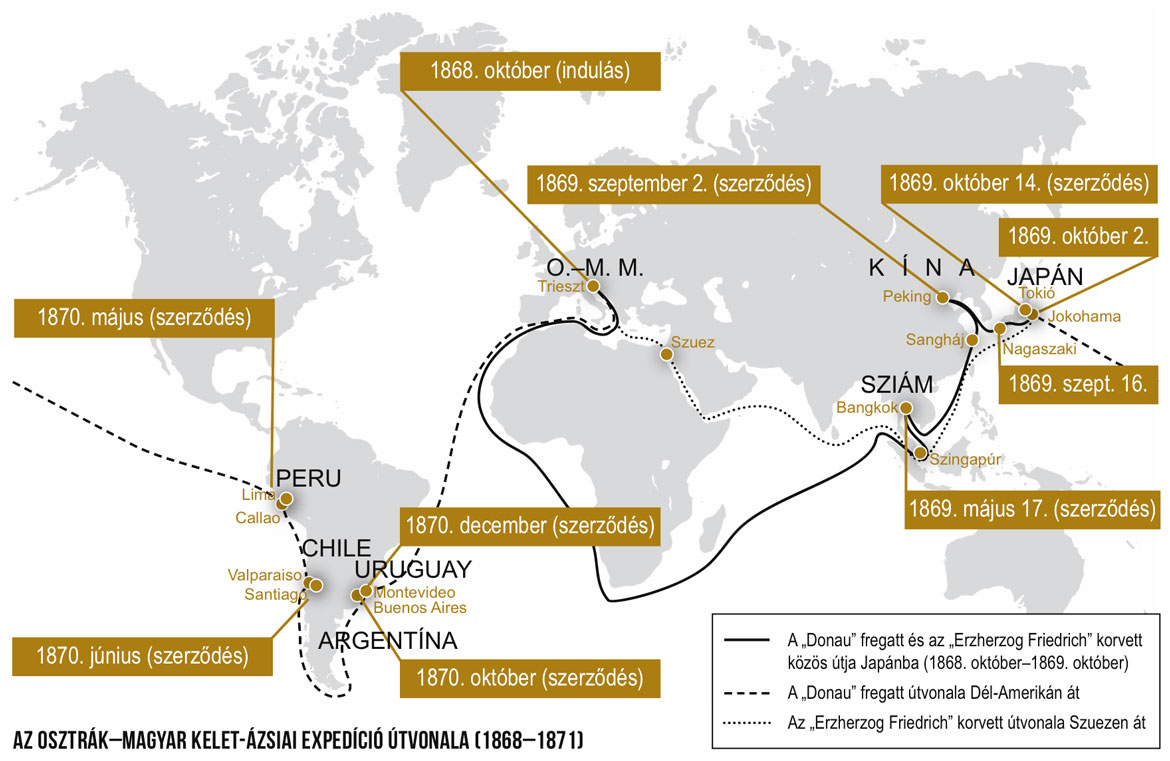
This paper gives a postcolonialist, critical geographical, and global historical re-interpretation of this expedition based on the travel writing of Xántus published during 1877–1886.[2] Against the dominantly biographical and documentary accounts on Xántus, which follow institutional or nationalist legitimation logics in presenting his “heroic” figure (focusing on his collections, personality and merits), this study instead engages with his activities in colonial networks, his descriptions of local industry and European export ambitions, and his global comparative ideas about colonialism and race, including comparisons between his local Hungarian, Eastern European, and Asian experiences. Whilst Xántus was known for his humanist critique of colonialism and solidarity with the colonially suppressed (especially in the case of North American Indians), his Asian travelogues shed light on his staunch support for the European colonial system, and how his activities relied on and contributed to national and imperial power networks and interests. In Borneo, he praised British colonialism against the Dutch, who “achieved success by resorting to the iron rod, absolute tyranny, and treaded ruthlessly upon all human rights (…), while England introduced to all its colonies English self-government, and shared its own freedoms with the conquered”.[3] As a prolific writer, he constructed his reporting credibility through various modalities, references, and practices, and contributed to a positive geographical imagination of the “fresh” and “juvenile” tropics ripe for exploration and exposed to masculine colonial practices of overcoming nature.[4] Swaying between imperialist Eurocentrism and anti-Eurocentric criticism, his depictions of the East fitted into the wider colonial discourse of European Orientalism, but through an Eastern European eye. His travelogues detailed the global political economy of the Hungarian diaspora, such as plantation workers, officers, traders, or the global remittance network of Gypsy and Sekler (székely) entertainers from Transylvania.[5]
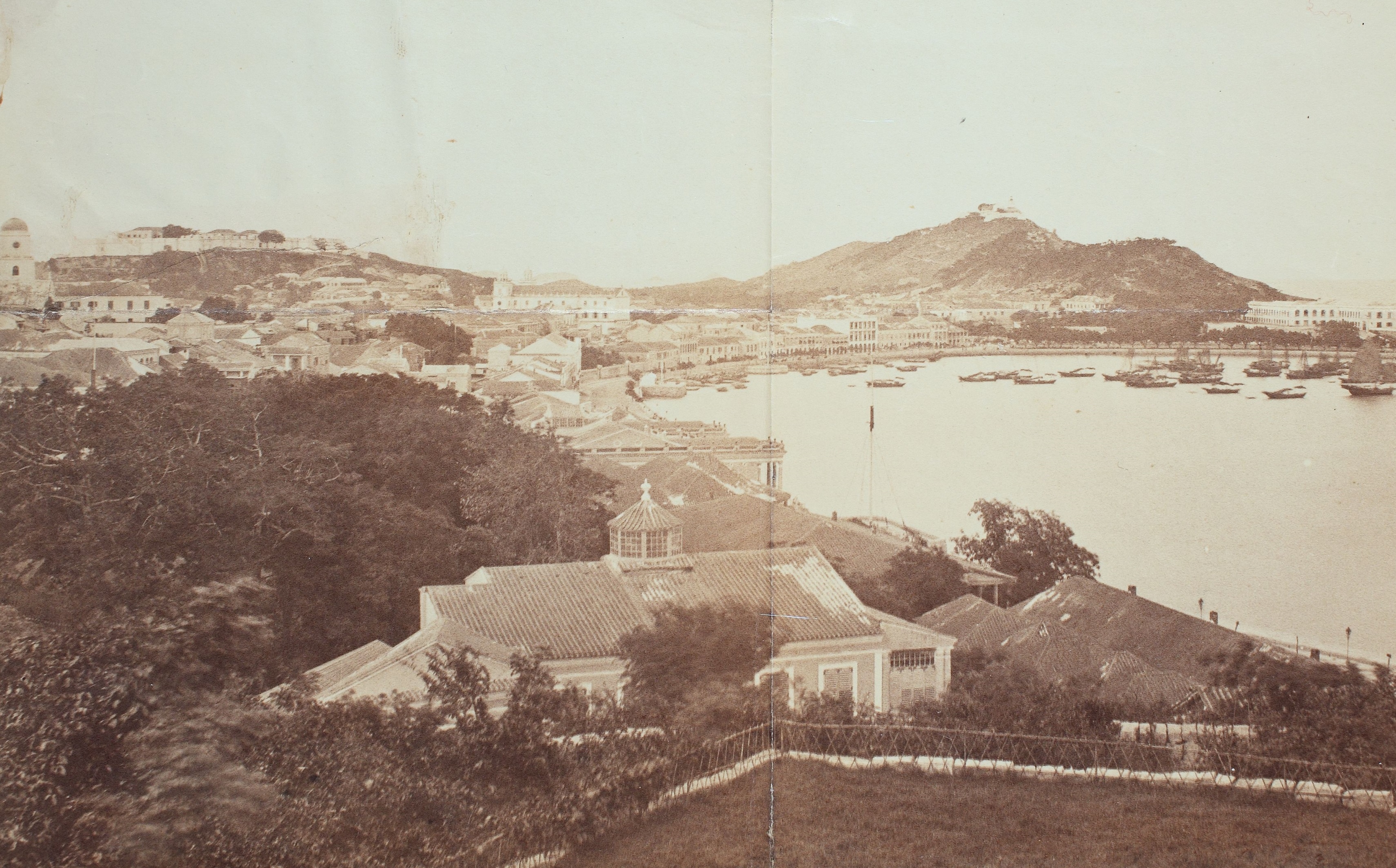

Source: Hungarian Museum of Ethnography.
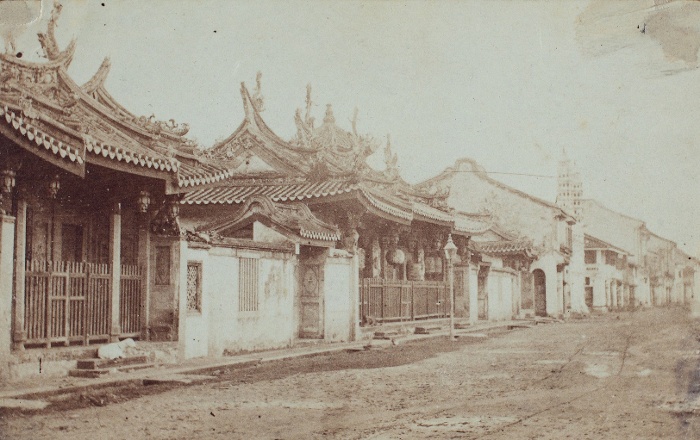

Source: Hungarian Museum of Ethnography.
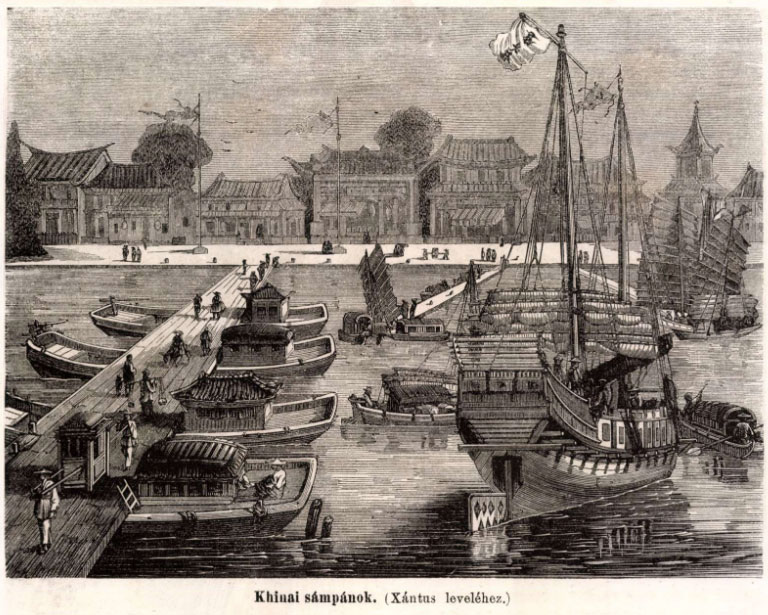

Source: Khinai sámpánok. (Xántus leveléhez) Hazánk s a Külföld, 6(10): 149.
In a wider historical context, the expedition of Xántus not only tells us much about how Hungarian geographical knowledge production was embedded in global colonialism, but also demonstrates the shift from reproducing dominantly Western geographic images of Asia towards developing an expansionist Hungarian Orientalism and Eurasian geopolitical vision between the late 19th and the mid-20th centuries. The newer generation of expeditions, such as by Benedek Baráthosi Balogh, Béla Széchenyi, Lajos Lóczy, Jenő Cholnoky, János Kovrig, or Viktor Keöpe, increasingly imagined Asia within a Turanist vision, an overarching geographical-cultural ideology of Hungarian-Asian racial brotherhood, which served as a semiperipheral imperialist globalisation strategy to counter or bypass Habsburg dependency and Western imperialism.
Xántus, through his popular figure as a prolific field-working scientist and a “national hero” who fought against the Habsburgs in 1848, was among the few “bourgeois” explorers to be early rehabilitated in the Communist era, since Habsburg rule was interpreted as a form of colonialism, and this history facilitated relations with decolonising Afro-Asian countries after WWII. But even today, discussion of Hungarian explorers’ colonialist and racist attitudes are absent from national collective memory, and as recent Chinese expansion with the New Silk Road and One Belt One Road macroprojects has reignited the Hungarian Orientalist heritage in culture and foreign policy, perhaps it is timely to re-evaluate the colonial history of Hungarian relations to Asia.

Source: Gyarmati, J. (2019): Xántus János, a gyűjtő. Honismeret, 47(6): 8–15.
[1] Ginelli, Z. (forthcoming): Global Colonialism and Hungarian Semiperipheral Imperialism in the Balkans. Manuscript.
[2] This paper also builds on the Xántus collection organized by the research project of János Gyarmati, “The Austro-Hungarian East Asia Expedition and the Collection of János Xántus”.
[3] Xántus, J. (1880): Borneo szigetén 1870-ben tett utazásomról. Földrajzi Közlemények, 8: 153–219. p. 156.
[4] Xántus, J. (1879): Uti emlékeim Singapoore és vidékéről. Győr: Özv. Bauervein Gézáné. p. 35–36.
[5] Ibid, p. 86–92.
Read a previous description of this project here.
© Copyright – Content is protected by copyright!
Citation:
Ginelli Z. (2020): Opening Hungary to Global Colonialism: János Xántus and Hungarian Orientalism in East and Southeast Asia. Critical Geographies Blog, 2020.03.07. Link: /2020/03/07/opening-hungary-to-global-colonialism-janos-xantus-and-hungarian-orientalism-in-east-and-southeast-asia


